What is the difference between Thunderbolt and USB Type C?
What is USB-C?
USB, which stands for Universal Serial Bus, is an industry standard that establishes specifications for cables, connectors, and protocols for connection, communication, and power supply between computers, peripherals, and other computers. There are several USB connectors, including USB-A, USB-B, Mini-USB, Micro-USB, and USB-C.
USB-C, or USB Type-C, is a contemporary connector system distinguished by its symmetrical design. It is primarily used to transmit data and power through a single cable. Additionally, USB-C can facilitate direct connections between two devices.
- USB-C stands out with its reversible design, allowing the connector to be plugged in any direction
- Supports impressive data transfer rates, reaching up to 20 Gbps with USB 3.2 Gen 2 2x2. Some newer versions may support even higher speeds.
- Capable of delivering up to 100 watts, suitable for charging devices from smartphones to laptops.
- Enables transmission of non-USB signals like DisplayPort, Thunderbolt, and HDMI, adding to its versatility.
USB Types and Speed
| USB Type | Speed |
| USB 1.0 | 1.5 Mbps |
| USB 2.0 | 12 Mbps |
| USB 3.0 | 480 Mbps |
| USB 3.1 Gen 1 | 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.1 Gen 2 | 10 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1x1 | 5 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2x1 | 10 Gbps |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 | 20 Gbps |
| USB4 | 40 Gbps |
What is a Thunderbolt?
Thunderbolt efficiently combines data transfer, video input/output, and power delivery into one cable. Thunderbolt 3 and 4, sharing the same physical design as USB-C port, integrate most USB-C functionalities and are even compatible with USB devices.
- Thunderbolt 3 and 4 offer remarkable speeds of up to 40 Gbps.
- Transferring large amounts of data, capable of handling video output for multiple 4K monitors at 60Hz.
- Provide up to 100W of power, suitable for charging a wide range of devices.
Thunderbolt Types and Speed
| Thunderbolt Version | Speed |
| Thunderbolt 1 | 10 Gbps |
| Thunderbolt 2 | 20 Gbps |
| Thunderbolt 3 | 40 Gbps |
| Thunderbolt 4 | 40 Gbps |
Compare Thunderbolt and USB-C generations
| Feature | Thunderbolt 3 | Thunderbolt 4 | USB 3.2 | USB4 |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps | Up to 40 Gbps | Up to 20 Gbps | Up to 40 Gbps |
| Display | One 4K monitors | Two 4K monitors or one 8K monitor | One 4K monitors | Two 4K monitors or one 8K monitor |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 100W | Up to 100W | Up to 100W |
| Daisy- Chaining | Up to 6 devices | Up to 4 devices | Not supported | Not supported |
| Passive cable length | 0.5m | 0.5m- 0.8m | 1m | 0.5m-1m |
| Connector | USB C | USB C |
USB C |
USB A, USB B and USB C |
Thunderbolt 3 and 4, while physically identical to the USB-C ports, the main difference of Thunderbolt is offering significantly higher data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps compared to the maximum 20 Gbps of USB-C 3.2 Gen 2x2. Both Thunderbolt versions can daisy-chain multiple devices and deliver up to 100W of power, but Thunderbolt 4 has stricter minimum performance requirements, including support for two 4K displays or one 8K display and enhanced security features. In contrast, USB-C is more universally adopted due to its compatibility with a wide range of devices and standards, including USB 2.0, 3.0, 3.1, and 4, but generally most types of USB don't offer the same high-speed capabilities (except USB4) or daisy-chaining functionality as Thunderbolt.
What Are Use Cases of Thunderbolt and USB-C?
Key use cases of Thunderbolt 3&4
Thunderbolts 3 and 4 are primarily used in high-performance and professional settings due to their exceptional data transfer speeds and versatile connectivity.
- Professional Video and Audio Production: Its high-speed data transfer is ideal for handling large video and audio files, essential in film production and music recording studios.
- Data-Intensive Workflows: thunderbolt is favored in fields like scientific research, data analysis, and graphic design, where large files and datasets are frequently transferred and processed.
- External Storage Devices: Connecting high-speed external drives for rapid data access and backup solutions.
- Daisy-Chaining Multiple Devices: Allows connecting multiple devices like hard drives, monitors, and audio interfaces to a single Thunderbolt port, reducing cable clutter.
Key use cases of USB C
USB-C's adaptability and capability to support multiple functions, including charging, data transfer, and AV output, make it a highly sought-after interface in both consumer electronics and professional equipment.
- Universal Charging: USB-C is used to charge a wide array of devices, from smartphones and tablets to laptops, due to its capability to deliver significant power (up to 100W).
- Data Transfer: Facilitates data transfer between devices such as computers, smartphones, external hard drives, and flash drives, supporting various data transfer speeds depending on the USB standard.
- Connecting Peripherals: Widely used to connect peripherals like keyboards, mice, printers, and external monitors. Its reversibility and uniformity simplify connections.
- Audio and Video Output: USB-C can transmit audio and video signals, allowing it to connect to external displays, TVs, and projectors, often through alternate modes like DisplayPort or HDMI.
- Consumer Electronics: Its adoption of a range of consumer electronics signifies a move towards a more universal and simplified connectivity standard across various devices.
Predicting the future of Thunderbolt and USB Type-C
The future of Thunderbolt and USB Type-C technologies is likely to significantly influence the industrial computer industry, driven by advancements and growing standardization. Thunderbolt is expected to see enhancements in speed, efficiency, wider adoption, integration with wireless technologies, and increased security features. These developments will cater to the grow rapidly data demands in various sectors.
USB Type-C, on its part, is anticipated to become more prevalent as a universal connectivity standard, with improvements in power delivery and data capabilities and potential convergence with emerging technologies like wireless charging. This evolution will facilitate greater standardization and compatibility in industrial computing, improve data management, reduce system complexity and costs, and enhance the flexibility and scalability of industrial computers, meeting the dynamic demands of industrial applications.
Key Markets That Benefit From Thunderbolt and USB Type-C
- Industrial and Automation
- Healthcare and Medical Imaging
- Creative and Media Industries
- Information Technology and Data Centers
- Gaming and Virtual Reality
- Professional and Consumer Electronics
C&T’s Industrial Grade Motherboards Support USB Type-C
C&T provides a variety of industrial motherboards that are versatile for applications such as medical, surveillance, digital signage, networking, industrial automation, and kiosks. These motherboards comply with industry size standards and mounting hole locations, ensuring seamless integration and upgrade compatibility.
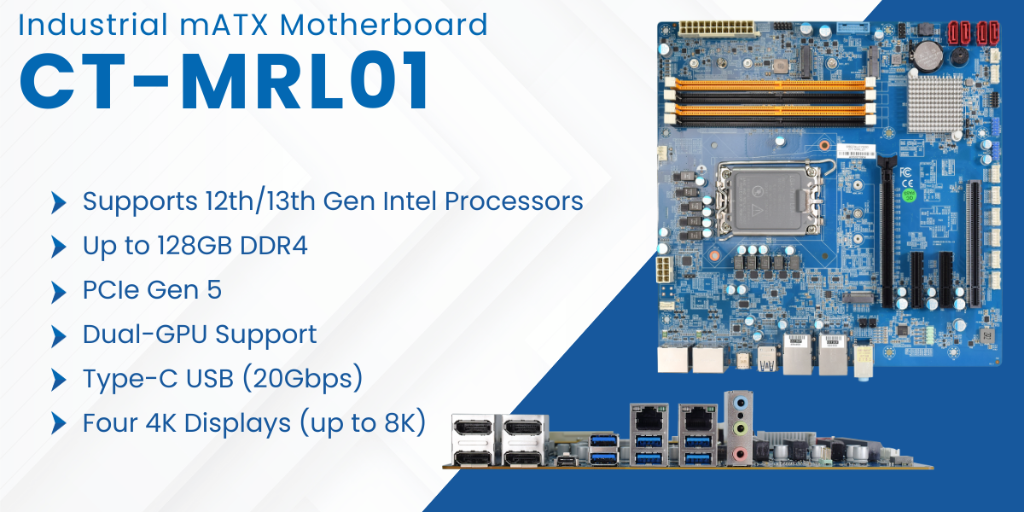
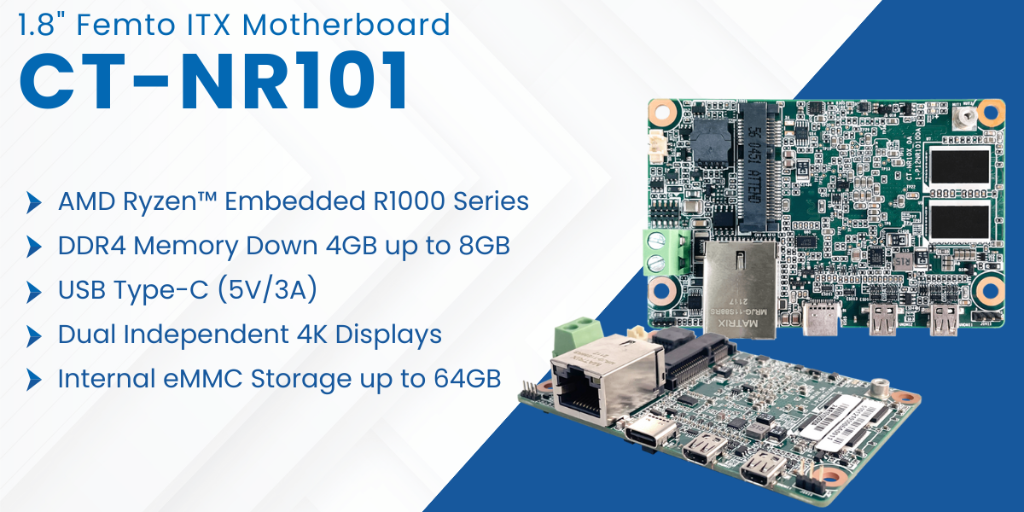
CT-MRL01- Micro ATX Motherboard
CT-NR101 1.8" Femto ITX Motherboard
FAQs:
Is USB-C the same as Thunderbolt?
No, USB-C is a type of connector, while Thunderbolt is a high-speed interface that can use the USB-C connector. Thunderbolt offers more advanced features like higher data transfer speeds and daisy-chaining capabilities.
Is USB C better than Thunderbolt?
"Better" depends on usage. USB-C is more universal and versatile for general use, while Thunderbolt, especially versions 3 and 4, offers higher performance for data-intensive tasks.
Is Thunderbolt faster than USB4?
Thunderbolt 3 and 4 offer speeds up to 40 Gbps, which is the same maximum speed as USB4. However, Thunderbolt 3/4 has more stringent requirements for consistent high-speed performance.
Is Thunderbolt for Apple only?
Thunderbolt is not exclusive to Apple. It was initially developed in collaboration with Intel and Apple, but it's available on various devices and motherboards across different brands.
Can I plug USB-C into Thunderbolt?
Yes, you can plug a USB-C device into a Thunderbolt port. The Thunderbolt port is backward compatible with USB-C devices and cables, but it will operate at USB-C speeds and capabilities.
Why is Thunderbolt 3 faster than USB-C?
Thunderbolt 3 is faster because it combines PCI Express (PCIe) and DisplayPort (DP) data transfer standards, along with USB 3.1, allowing for higher bandwidth and thus higher data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps.