What is SCADA System?

Table of contents:
- What is SCADA?
- Key Components of SCADA System
- How SCADA system works
- SCADA System Applications
- The Importance of SCADA System
- DCS vs SCADA: Which is Better?
What is SCADA?
A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system is an advanced framework used to manage, monitor, and analyze industrial operations and equipment. Comprising an integrated suite of software and hardware components, SCADA systems enable comprehensive data acquisition from industrial devices, both on-site and remotely, ensuring optimal operational control and efficiency.
Key Components of SCADA System
Hardware Components:
- Sensors and Actuators: Devices that gather data like temperature and pressure, and perform actions based on commands.
- Remote Terminal Units (RTUs): Connect sensors to the central system, manage data collection, and control local devices.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): Handle complex tasks and manage more data points, providing flexibility and enhanced processing power.
- Communication Equipment: Facilitates data transfer between field devices and the control center using various protocols.
Software Components:
- SCADA Software: Runs on servers at the control center to process data, monitor in real-time, and support data visualization via interfaces.
- Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs): Graphical interfaces that display real-time data, allowing operators to quickly assess and make decisions.
How does SCADA system work?
Data Acquisition → Monitoring → Control → Data Analysis and Reporting → Alarm Systems
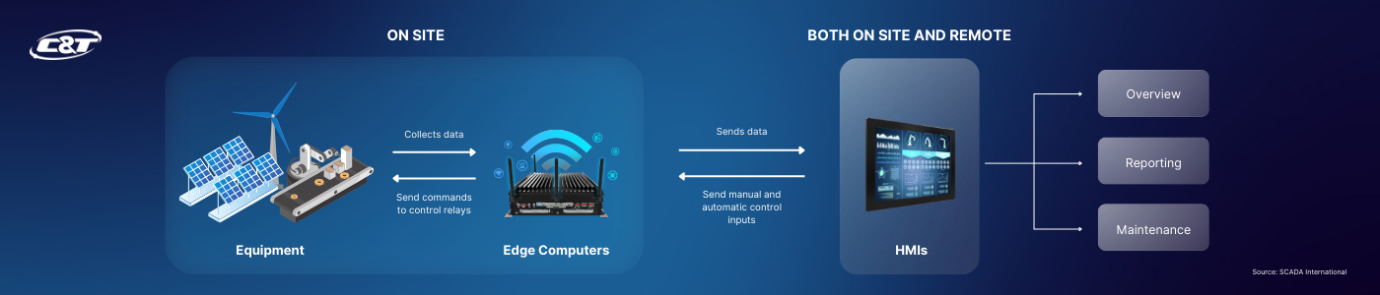
A SCADA system workflow involves collecting data from field devices using PLCs, RTUs and Edge Computers, which then transmit this data to a central HMI for monitoring and analysis. The HMI displays the information in a user-friendly format, allowing operators to quickly understand and react to operational data and alarms.
Operators can also send control commands back through the system to manage equipment and processes remotely, enhancing operational efficiency and responsiveness. Some SCADA systems also offer automated controls and reporting features to further streamline operations.
What is SCADA system used for?
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system is primarily used for monitoring and controlling industrial processes and infrastructure in real-time. Here are some key applications:
► Utilities
In utilities like electricity, water, and wastewater management, SCADA systems help monitor and control the infrastructure that delivers these essential services. They manage everything from electric grids, ensuring consistent power distribution and outage management, to water purification and sewage treatment processes, optimizing performance and environmental compliance.
► Oil and Gas
SCADA systems in the oil and gas industry are critical for monitoring pipelines, managing remote drilling sites, and overseeing refinery operations. They ensure efficient flow of oil and gas from extraction points to refineries and finally to distribution, enhancing safety by detecting leaks or potential failures early.
► Manufacturing
In manufacturing, SCADA systems optimize production lines, maintain quality control, and manage inventory. They allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments to the manufacturing process, increasing productivity and reducing downtime in factories.
► Transportation
SCADA systems facilitate efficient transportation management, whether it's coordinating train schedules and signaling in railways, managing logistical operations at airports, or controlling urban traffic lights and systems. They enhance safety, reduce congestion, and improve the overall flow of transportation networks.
► Renewable Energy
In the renewable energy sector, SCADA systems are used to monitor and optimize the performance of wind turbines and solar panels, manage their integration into the power grid, and perform predictive maintenance. This maximizes energy output and efficiency, crucial for the reliability and economic viability of renewable energy sources.
Why is SCADA system important?
SCADA systems are crucial for enhancing operational efficiency, safety, and reliability in industrial settings. They enable real-time monitoring, automated control, data analysis, and remote management, significantly reducing costs and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while adapting easily to changing operational needs. For example, an oil and gas company utilized a SCADA system to remotely manage and control its offshore drilling platforms. This capability allowed centralized engineers to adjust operating parameters in real-time, reducing the need for on-site visits and lowering operational risks, ultimately saving the company millions in annual maintenance costs.
DCS vs SCADA: Which is better?
A SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system is designed for monitoring and controlling industrial processes over large geographical areas, making it ideal for utilities and infrastructure management. In contrast, a DCS (Distributed Control System) is tailored for continuous and precise control within industrial plants, focusing on complex, high-speed processes in sectors like chemical production and power generation.
| Aspect | DCS | SCADA |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Focuses on continuous, precise control of processes within a facility | Focuses on monitoring and control over large geographical areas for a variety of processes |
| Architecture | Hierarchical and centralized within the plant, emphasizing control | Decentralized, suitable for extensive area applications, emphasizing data acquisition |
| Applications | Used in process industries (chemical, pharmaceutical, food, etc.) | Used in utilities and infrastructure management (electricity, water, oil and gas, etc.) |
| Real-Time Operation | Prioritizes fast response and continuous control | Handles real-time data but with a greater focus on supervision and less on immediate control |
| System Focus | Manages detailed control loops and process integrity | Manages data collection, site monitoring, and control at a more aggregated level |
| Typical Use Cases | Managing production lines, chemical reactions, and other complex processes | Monitoring pipelines, electrical grids, and remote installation |
Ultimately, the choice between SCADA and DCS should be based on the specific operational requirements, the complexity of the processes involved, and the geographic distribution of the assets. Each system provides unique benefits tailored to different types of industrial environments.

