What are Alder Lake CPUs?

Table of contents:
- What is Alder Lake?
- What is a Hybrid-Core Architecture?
- P & E Cores
- What is Alder Lake-N?
- Why N97? (N97 Vs Pentium 7505)
- What is Intel I3-N305?
- Low Power Consumption
- C&T's Intel Alder Lake N97 Product Line
What is Alder Lake?
Launched in late 2021, Intel's 12th Generation Core™ processors, nicknamed Alder Lake, introduced a fresh approach to computer processing. These processors are special because they mix two types of cores—high-performance cores for demanding tasks and power-efficient cores for less intensive activities—within a single chip. This blend is designed to provide a balance of high performance and low power use across different types of computer activities.
Alder Lake chips are built with Intel's advanced 10nm Enhanced SuperFin technology, which means they're designed to be faster, more power-efficient, and more adaptable than older versions. They support both new and old memory types (DDR4 and DDR5), the latest PCIe 5.0 standard for faster data transfer, and fit into the LGA 1700 socket, broadening their compatibility with various computers like laptops, desktops, and possibly even servers.
What is a Hybrid-Core Architecture?
Intel Alder Lake processors feature a hybrid-core architecture that integrates two distinct types of CPU cores on the same chip: Performance cores (P-cores) and Efficiency cores (E-cores). This design allows the processor to smartly switch between P-cores and E-cores depending on the task demands and the need for power efficiency. By dynamically adjusting which cores handle which tasks, the system can achieve optimal performance for intense computing while maintaining energy efficiency for less demanding activities. This leads to several benefits, including better processing power, cooler running temperatures, longer battery life, and more. Furthermore, Alder Lake processors are designed to work seamlessly with certain operating systems and applications to maximize the benefits of this hybrid architecture, thereby boosting overall system performance.
P & E Cores
Performance Cores (P-cores):
- These cores are built for high-demand computing activities like gaming, video editing, and intense multitasking.
- They excel in handling tasks that require fast processing of one thing at a time (single-threaded performance), offering high speeds and efficient processing (high Instructions Per Cycle or IPC).
- P-cores have larger memory stores (caches) and more processing pathways (execution units) than efficiency cores, allowing them to perform complex tasks quickly.
- These cores kick into action when the computer needs to run challenging applications smoothly, ensuring top performance for demanding tasks.
Efficiency Cores (E-cores):
- E-cores prioritize saving energy and are best for lighter tasks, running background activities, and managing power when the computer is not doing much (idle states).
- They run at slower speeds and use much less power than performance cores, which helps extend the battery life of portable devices and lowers energy use in desktops.
- These cores manage routine background activities like syncing emails, browsing the web, and maintaining the system, all while keeping power use low.
- They activate during lighter work or when the computer is idle, helping to save energy while still keeping the system responsive.
What Is Alder Lake-N & Why Efficiency Cores?
Historically, Intel's "N" suffix has indicated processors that are low-power or ultra-low-power, primarily designed for notebooks or other mobile devices. These processors are engineered to be energy-efficient while still providing sufficient performance for general computing tasks. The question then arises: if Alder Lake CPUs are distinguished by their hybrid architecture, why does Intel also offer an “-N” series that only includes efficiency cores?
To address this, it's essential to examine the characteristics of the efficiency core itself. Interestingly, the efficiency core isn't just about conserving energy; it's quite capable in terms of performance. Each efficiency core comes with 6MB of Smart Cache memory and is fundamentally a fourth-generation Atom processor, renamed from "Grace Mont." Unlike the performance cores, these do not have hyperthreading technology, which means they cannot split each physical core into two virtual cores for multitasking. Despite this, the efficiency cores are highly effective, delivering excellent performance efficiently. Intel labels it as “the world’s most efficient x86 core,” which outperforms even Intel’s most advanced architectures in terms of instructions per clock. This high efficiency allows Intel to offer the “-N” line within the Alder Lake series, specifically targeting scenarios where energy efficiency and lower power consumption are crucial, yet still requiring reliable performance.

Image source: Intel
Why N97? (N97 Vs Pentium 7505)
To really grasp how effective the Alder Lake E-core is, let's examine the Intel N97 (Alder Lake - N) and compare it with the 11th Gen Intel Pentium 7505 (Tiger Lake –U). This comparison will illuminate the unique capabilities of the E-core, as both processors share some similarities, yet exhibit distinct strengths and weaknesses.

The Intel Pentium 7505, part of the 11th Gen Tiger Lake –U series, boasts impressive features like support for up to 64GB of memory, a top speed of 3.5 GHz, and a reasonable thermal design power (TDP) of 15W. At first glance, the specs of the Pentium 7505 might seem superior to those of the N97. However, the N97 actually outperforms it in key areas.
Performance Difference
| Alder Lake (N97) | Tiger Lake (Pentium 7505) | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Specifications | ||
| Lithography | 10nm SuperFin | 10nm |
| Cores | 4 | 2 |
| Processor Base Frequency | 2.00 GHz | 2.00 GHz |
| Burst Frequency | 3.40 GHz | 3.50 GHz |
| L2 Cache Memory | 4.00 MB | - |
| L3 Cache Memory | 6.00 MB | 4.00 MB |
| TDP | 12W | 15W |
| Memory Specifications | ||
| Max Memory Size | 16GB | 64GB |
| Memory Type | DDR5-4800 | LPDDR4-3733 |
| Graphic Specifications | ||
| GPU Frequency | 120 GHz | 0.30 GHz |
| Max GPU Memory | 8GB | 32GB |
| Maximum Displays | 3 | 4 |
From the information provided, we see that the 7505 boasts a higher frequency, supports hyperthreading, and can handle larger memory sizes. However, the N97 excels in other significant areas. It supports the newer DDR5 memory type and is more energy-efficient, which are crucial factors in its overall superior performance.
Adding to its advantages, the N97 is designed to be a "smarter" CPU by optimizing power usage while efficiently managing background tasks and workloads. In comparison to older processor generations like Skylake, the N97 features:
- Increased instructions per clock (IPC): This means the processor can complete more tasks within a single clock cycle, enhancing its performance efficiency
- Improved branch prediction: This feature allows the processor to better anticipate the directions of future operations, minimizing unnecessary processing and boosting speed
- Enhanced vector instructions: These enable the processor to handle multiple data elements at once, speeding up complex tasks such as image and video processing
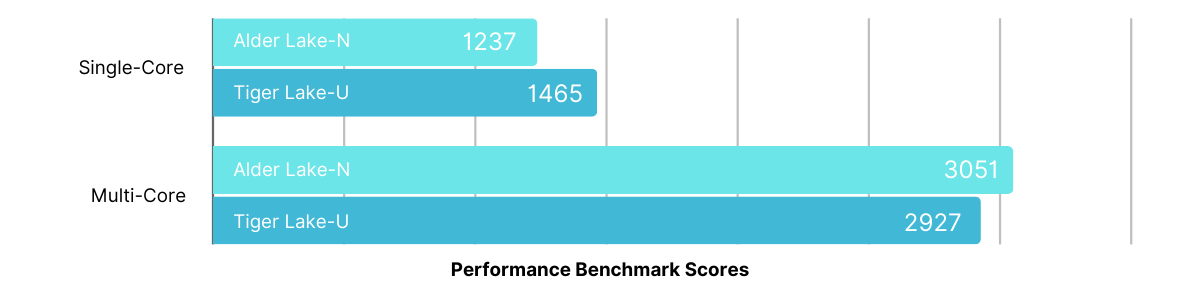
Although the overall benchmark scores of both processors are similar, it's important to consider other factors. The N97 excels in managing workloads, supports faster DDR5 memory, consumes less power, and is 34% less expensive than the 7505, according to Intel. Given these processors are often used in applications where heat and budget are limiting factors, the N97 stands out as the more advantageous choice.
Then What is Intel I3-N305?
The Intel Core i3-N305 is part of the 12th Gen Alder Lake – N series. Like other processors in this family, it focuses on low power consumption and efficiency, but still maintains the performance standards expected of a Core i3.
I3-N305 vs N97
| Alder Lake (i3-N305) | Alder Lake (N97) | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU Specifications | ||
| Lithography | Intel 7nm | 10nm SuperFin |
| Cores | 8 | 4 |
| Processor Base Frequency | 1.80 GHz | 2.00 GHz |
| Burst Frequency | 3.90 GHz | 3.40 GHz |
| L2 Cache Memory | 8.00 MB | 4.00 MB |
| L3 Cache Memory | 6.00 MB | 6.00 MB |
| TDP | 15W | 12W |
| Memory Specifications | ||
| Max Memory Size | 16GB | 16GB |
| Memory Type | DDR5-4800 | DDR5-4800 |
| Memory Bandwith | 76.8 GB/s | 38.4 GB/s |
The i3-N305 has twice as many efficient cores as the N97 and its earlier version, the N300, boasting 8 Alder Lake-N efficient cores. These cores are designed for low power use while efficiently managing background tasks and overall workload. This processor emphasizes efficiency rather than sheer power, but still delivers higher instructions per clock (IPC) and improved branch prediction compared to older i3 models, ensuring better performance for each watt of power used.
Strengths of the i3-N305:
- 8 Efficient Cores (Alder Lake-N): The increased number of cores significantly boosts performance for various workloads
- Higher Burst Frequency (3.80 GHz): Offers quicker responsiveness and speedier task execution
- Improved Intel 7nm Process: Similar to the N97, this process enhances transistor density, which helps in reducing power consumption
- Supports DDR5 Memory: Depending on the system setup, it can handle more data at once, improving performance over systems like the N97
- Fanless Designs: Its low power consumption enables the design of fanless systems, which are dependable and suitable for tough industrial environments.
Low Power Consumption
To fully appreciate the significance of the Alder Lake-N processors like the N97, it’s essential to focus on one of their key attributes: low power consumption. This feature is vital for several important reasons, particularly in relation to its intended applications:
- Enabling Thin and Light Hardware Design: The low power consumption of the N97 means it generates less heat, often removing the need for large cooling fans. This allows for the development of slim, light devices that are easier to carry and more durable
- Extended Battery Life: Using less power means the battery lasts longer. This is especially important for users who need their devices to operate for extended periods when on the move
- Fanless Designs: The N97’s ability to operate on low power is perfect for devices that require quiet operation and durability, as it supports designs without cooling fans. Such designs are ideal for harsh industrial environments where durability is a priority.
- Improved Thermal Management: With lower power usage comes less heat production, which simplifies managing the device’s internal temperature. This can lead to more reliable operation and a longer lifespan for the device.
Thus, the N97’s low power consumption is not just a minor spec; it’s a crucial aspect that supports the processor’s main functions, ensuring efficient and effective performance.
C&T's Intel Alder Lake N97 Product Line
-
BCO-1000-ADLN Series
X86 semi-rugged computers that are powered by Intel Alder Lake N97 CPU with rich I/O configuration.This powerful CPU performance positions it as an optimal choice for demanding industrial edge IoT applications, seamlessly providing cost-effective and deployment-ready solutions
-
HIO-200 Series New!
The HIO Open Frame Panel PC features exceptional screen readability and clarity, with a front panel that is IP65 rated and a 7H scratch-resistant surface. Powered by the Intel Alder Lake N97 processor, it delivers robust performance for demanding applications. Available in three sizes: 10.1", 15.6", and 21.5".
-
AIO-200 Series New!
Capacitive All-in-One Touch Panel PC featuring a front panel rated IP65 for water resistance and a back panel rated IP54 for dust protection, complemented by a 7H scratch-resistant surface. It's powered by the Intel Alder Lake N97 processor and is available in three sizes: 10.1", 15.6", and 21.5".




