Navigating The Differences Between LTE, 4G and 5G
Embarking on a journey through the corridors of mobile network evolution, we encounter LTE, 4G, and 5G—three pivotal chapters in the connectivity story. From the inception of Long-Term Evolution to the lightning-fast speeds of 5G, each generation has reshaped the communication landscape, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and transformative possibilities. Let's delve into the essence of these technologies, exploring their evolution, capabilities, and the promising horizons they hold for the future of connectivity.

Evolution of Mobile Network Technologies
The journey begins with the introduction of 3G, which laid the groundwork for mobile data connectivity but needed to improve its speed and reliability. The subsequent emergence of LTE (Long-Term Evolution) marked a significant leap forward, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and enhanced performance. Building upon the success of LTE, the arrival of 4G further revolutionized the mobile experience, paving the way for seamless streaming, gaming, and communication. And now, with the dawn of 5G, we stand on the brink of a new era characterized by unparalleled speed, ultra-low latency, and transformative possibilities.
LTE (Long-Term Evolution)
LTE stands for Long-Term Evolution, a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals. LTE is often called 4G LTE because it is the fourth generation of mobile network technology, succeeding 3G technology. LTE was first commercially deployed in 2009, marking the beginning of the transition from 3G to 4G technology.
With its advanced technology and efficient spectrum usage, LTE enables users to enjoy faster downloads, smoother streaming, and more responsive applications. Despite its strengths, LTE does have limitations, particularly in terms of coverage and capacity, which have paved the way for the development of subsequent generations.
Advantages
- Wide Coverage: Ensures high-speed internet access in areas beyond 4G or 5G reach.
- Enhanced Connections: Boosts network efficiency and supports numerous users.
Disadvantages
- Speed Limitations: Slower compared to 4G and 5G peak speeds.
- Variable Performance: Depends heavily on location and network status.
- Upgrade Costs: Device upgrades necessary for full LTE benefits can be expensive.
4G
4G, short for Fourth Generation, is the fourth generation of mobile network technology standards. It succeeds the previous generations of mobile networks, including 3G (Third Generation).
Building upon the foundation laid by LTE, 4G represents a significant milestone in mobile connectivity, offering enhanced speed, reliability, and efficiency. With 4G networks, users can experience seamless connectivity, even in densely populated areas, thanks to advancements in spectrum utilization and network optimization. Whether streaming HD videos, playing online games, or conducting video calls, 4G networks provide the bandwidth and stability required for various applications.
Advantages
- High-Speed Data: Enables faster streaming, downloading, and browsing.
- Increased Capacity: Supports more users and services at once.
- Reduced Latency: Delivers lower latency compared to LTE
Disadvantages
- Inconsistent Coverage: Some areas lack 4G service.
- Battery Drain: Faster speeds increase battery consumption.
- High Deployment Cost: The infrastructure investment affects costs for both providers and consumers.
5G
5G, short for Fifth Generation, is the latest generation of mobile network technology standards, succeeding 4G, it is also the newest connectivity technology today. 5G technology represents a significant leap forward in terms of speed, capacity, and connectivity compared to its predecessors, offering transformative possibilities for various industries and applications such as autonomous vehicles, remote healthcare, and immersive experiences.
Its advanced technologies, including millimeter-wave spectrum and massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), are poised to unlock new possibilities and drive innovation across various sectors. While still in the early stages of deployment, 5G is rapidly expanding globally, offering users unparalleled speed, reliability, and connectivity for a wide range of applications and services.
Advantages
- Ultra-High Speed: Achieves speeds up to 20 Gbps for rapid data transfer.
- Minimal Latency: Reduces response time to about 1 ms, enhancing connectivity.
- Massive Connectivity: Supports extensive device connections, boosting IoT growth.
Disadvantages
- Limited Rural Coverage: Initially focuses on urban areas, leaving rural zones behind.
- Substantial Costs: Infrastructure and development come with high expenses.
- Device Compatibility: Necessitates the acquisition of new, 5G-compatible devices.
The difference between LTE, 4G, and 5G
LTE vs 4G vs 5G Comparision
| Feature | LTE | 4G | 5G |
| Speed | 3Mbps- 100 Mbps | 100 Mbps- 1000 Mbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 15- 50 ms | 30 ms to 70 ms | As low as 1 ms in ideal conditions |
| Frequency Bands | Various (700 MHz to 2.6 GHz) | Various (700 MHz to 2.6 GHz) | Sub-6 GHz and mmWave |
| Coverage | Widespread | Widespread | Expanding |
| Deployment Stage | Mature | Mature | Early |
| Application Areas | Enhanced mobile web access, IP telephony, gaming services, high-definition mobile TV, video conferencing, and 3D television. | Improved mobile internet experience, higher speeds for video streaming, and higher-quality video calls. | Enables ultra-reliable low-latency communications (URLLC), massive machine-type communications (mMTC), and enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB), facilitating new applications like IoT, autonomous vehicles, and smart cities. |
When comparing LTE, 4G, and 5G, several factors come into play, including speed, latency, coverage, and applications. While LTE offers reliable performance and widespread availability, it needs to improve in speed and latency compared to 4G and 5G. On the other hand, 4G networks provide faster speeds and lower latency than LTE, making them ideal for bandwidth-intensive tasks. However, it's 5G that truly stands out, boasting blazing-fast speeds, near-instantaneous response times, and the potential to connect billions of devices seamlessly.
Is 5G more popular than 4G in the near future?
Generally, 4G has been more widely adopted and entrenched in the global market due to its extended existence and broader coverage. However, as 5G deployments expand, its popularity steadily increases. Especially in the US, According to GlobalData, 5G is poised to surpass 4G as the preferred method of accessing mobile internet in the US by 2024. This shift will see more subscribers opting for 5G services than 4G. Furthermore, data consumption among 5G subscribers is projected to outpace 4G users by 2023, with 5G accounting for 80.8 million terabytes (TB) of mobile broadband traffic, compared to 4G's 75.7 million TB.
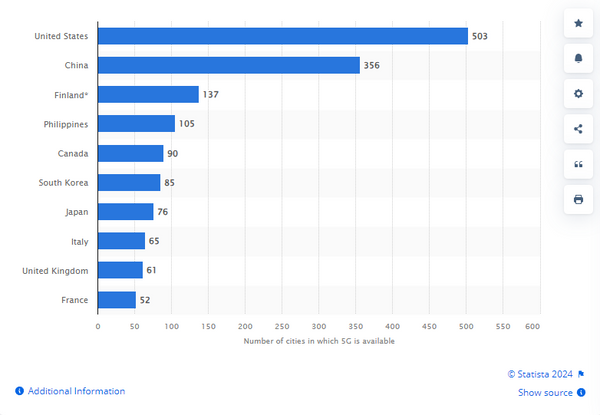
Number of cities in which 5G is available 2023 by country
Does 6G already exist?
Looking ahead, while 5G is on the cusp of becoming the new standard, discussions about the future of connectivity are already underway. Some experts are beginning to speculate about the potential of 6G technology, envisioning even faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity than ever before. While 6G remains conceptual mainly at this stage, its emergence could unlock new realms of possibility, powering innovations that we can scarcely imagine today. As we stand on the brink of this technological frontier, the horizon of connectivity stretches ever further, promising a future where seamless, high-speed communication is not just a luxury but a fundamental aspect of daily life.
What are the roles of 4G,5G in Industrial Automation Infrastructure?
4G and 5G technologies serve as foundational pillars for the evolution of Industrial Automation Infrastructure, each playing distinctive roles in this transformation. 4G laid the initial groundwork, offering reliable high-speed connectivity that enabled the expansion of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), facilitated remote monitoring and control, and integrated cloud-based data analytics into industrial operations. 5G, building on this foundation, introduces significantly enhanced capabilities including higher speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive device connectivity, crucial for real-time automation and control in smart factories. It brings innovations such as Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication (URLLC), Massive Machine Type Communications (mMTC), network slicing for customized virtual networks, and edge computing, which processes data closer to its source. Together, 4G and 5G are pivotal in advancing industrial automation, leading to the creation of highly efficient, automated, and intelligent manufacturing environments.
Industrial Computer System with Dual SIM 5G, 4G, and LTE

C&T's product line seamlessly integrates 4G and 5G modules into industrial computer systems. By incorporating these modules, our computers offer stable internet connections via cellular networks, serving as an alternative or complement to traditional wired setups. This integration empowers IPCs to enable remote monitoring, control, and data transmission across a wide range of applications, spanning industrial automation, smart manufacturing, transportation, and IoT deployments. With this enhanced connectivity, businesses can facilitate real-time communication, seamless data exchange, and access to cloud services, empowering them to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and boost productivity in dynamic and challenging environments.
Explore 5G Industrial Computer Solutions
In conclusion, while 4G and LTE have brought significant improvements to mobile networks, it's evident that 5G is now the leader in terms of speed and reliability. With its virtualized infrastructure, low-latency connectivity, and unmatched data transfer rates, 5G technology offers a monumental leap forward for high-end computing applications operating within today's interconnected ecosystem. Its advanced analytics capabilities further highlight its potential to revolutionize various industries by efficiently managing complex data. As we enter the era of 5G, we embark on an exciting journey where connectivity knows no bounds, opening endless possibilities for innovation and progress.

