Knowledge Center
07.Apr.2021
Rugged Industrial Computers For Extreme Deployments

Industrial applications are implementing advanced technologies that have rapidly grown over the past several years and the trend keeps increasing exponentially. To cope with these software and hardware advancements, manufactures are challenged to produce more powerful computers. Furthermore, these computers are also required to be reliable and durable amid industrial deployments at the edge in extreme environments. This explains the surging demand for rugged PCs on the market. That said, after reading this article you will understand what is a rugged computer and what makes it truly rugged.
What Is A Rugged PC?
A rugged PC is a computer that is built tougher than any other PC. It is engineered and built specifically to perform extraordinarily in the harshest environments where regular consumer-grade computers cannot withstand. Nothing extraneous, everything about it is constructed to maintain its durability, reliability, and longevity amid deployments.A rugged computer is unique and has a distinctive architecture. Their robust structure is supported by their fanless, cable-less, and one-piece design. Thus, rugged PCs can withstand intense environments where they will be exposed to extreme temperature, shock, vibration, tiny dust particles, water exposure, and many other challenging conditions. What makes them so appealing is regardless of their rugged design, great rugged PCs are also remarkably versatile, expandable, customizable, and flexible. This is why plenty of industries are benefiting from ruggedized pcs for their application instead of desktop processors.
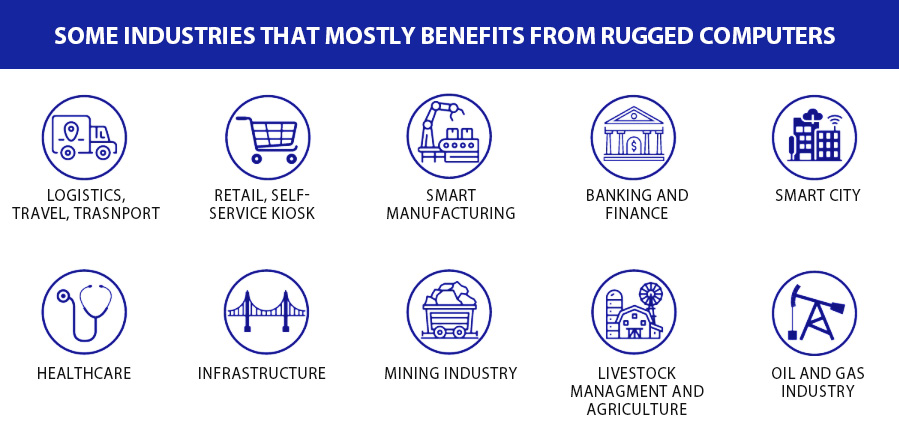
Industries That Utilize And Benefits From Rugged PCs
Understanding Rugged PC's Designs And Capabilities - When Rugged Meets Fanless
Rugged devices are built with sturdy materials, but they are still semi-rugged. For a rugged PC to be fully rugged engineers need to make sure they eliminate moving parts within the computer’s architecture. This is where they implement a fanless design for the rugged PC to be ultra-rugged. Fanless or passive cooling design works by cooling the device without a fan but instead utilizes heat sinks to dissipate heat from the CPU and motherboard. The heat sink transfers the heat from the electronics to the computer’s metal chassis. The external chassis is specially designed to protect and dissipate heat naturally into air. With the whole chassis working as a passive cooler, the PC can control its heat effectively without requiring any fans.
Moreover, the fanless design offers various benefits and reduces the possibility of a computer malfunction Without installing any fans, it will extend the PC MTBF (meant time between failure) and prevent failure caused by the fan. There will be no need for repair or to replace the fan itself. When utilizing passive cooling, the computer wouldn’t need any venting holes and this can increase the ingress, protecting the system from the ingress of dust and other small particles. Moreover, it’s more convenient to have a silent PC even when processing heavy workloads of data.
Extreme Temperature Range
Ruggedized PCs are capable of withstanding extreme environments because there are heatsinks that are made out of extra-conductive materials (aluminum and copper) attached to their CPUs and SoCs, conducting the heat to their outer enclose that is made out of extruded aluminum with heavy-duty metals.The outer enclosure or chassis then dissipate heat to the external airflow and also functions as a robust structure to protect the computer from shocks and vibrations. In this way, rugged computers can maintain their reliability and durability amid deployments in extreme heat environments from the scorching hot desert to the freezing cold poles of the earth.
Military Standard - Shock And Vibration
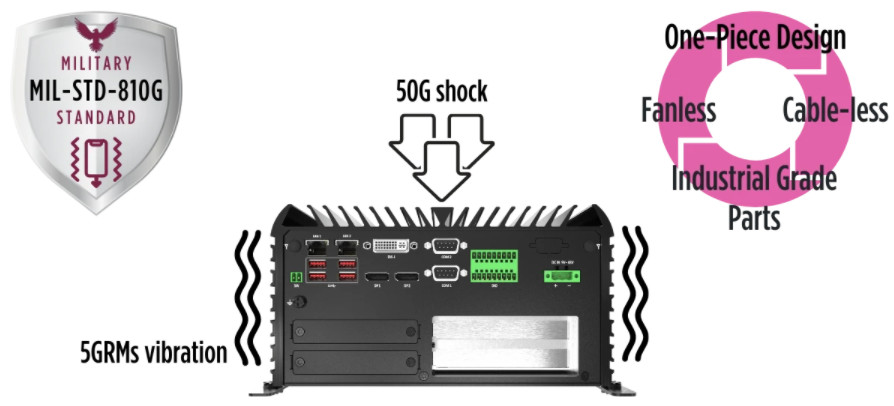
To ensure extra durability, reliability, and longevity, rugged PC architecture is designed to be resistant against extreme shock and vibration. Great rugged PCs are compliant with the military standard (MIL-STD-810G) in shock and vibration resistance. It even surpasses the test’s standards capable of sustaining 50Gs of shock, Half sine, 11ms (with SSD) for shock, and 5 GRMs of vibration, 5-500Hz, 0.5hr/axis (with SSD) for vibration. Built out of fanless, cable-less, and one-piece design makes the rugged PC extremely tough.
Furthermore, rugged PCs are utilizing industrial-grade components (such as capacitors, resistors, power chokes, etc.) that are strictly selected for the best performance possible. Also, rugged PCs use SSDs instead of HDDs to fully eliminate moving parts within the construction. Extreme shocks and vibrations can easily damage or loosen both the internal and external components of the PC and cause fatal failures. Therefore, when moving parts are completely taken out of the equation, the removal eliminates the potential failures that are caused by the system being exposed to heavy shocks and constant vibrations.
Solid Protection On Dust And Water – IP Rating
Rugged PCs are rated as IP65 up to IP69K in IP rating, which is the highest score for both dust and water protection. This is achievable due to the implementation of a fanless design. Graded with a high IP rating makes rugged PC perfect for deployments where devices will face frequent washdowns such as in the mining industry, automotive industry, health industry, and food and beverage processing industry.
Versatility | Power Control
To add more versatility, rugged PCs are compatible with a wide range of voltage for power input, ranging from 9V up to 48V so that they can be deployed in any situation that generates higher or lower voltages into the system. Moreover, rugged PCs are equipped with power ignition management for a wider application such as deployments on a vehicle or mobile environment. It intelligently manages the in-vehicle computer’s power supply when starting up or shutting down the vehicle. This averts the risk of improper shutdown and losing sensitive data from an unexpected power outage. With intelligent power management systems, a rugged PC can ensure reliable and dependable applications across a wide range of industries.
Expandability & Flexibility | Compact Design & I/O Ports
Rugged PCs are considerably compact in design that allows them to save more space to fit in a tight space. Despite being compact in design, systems can be expanded to meet the application’s needs. Rugged PCs are capable of supporting I/O, storage, and memory expansions. Therefore, you can increase the computing capabilities by adding memory, storage, adding new input ports that are specified based on your specific needs. With PCIe 4.0 connection protocol, additional GPU, and a M.2 NVMe SSD, processing and transferring data will be much faster.
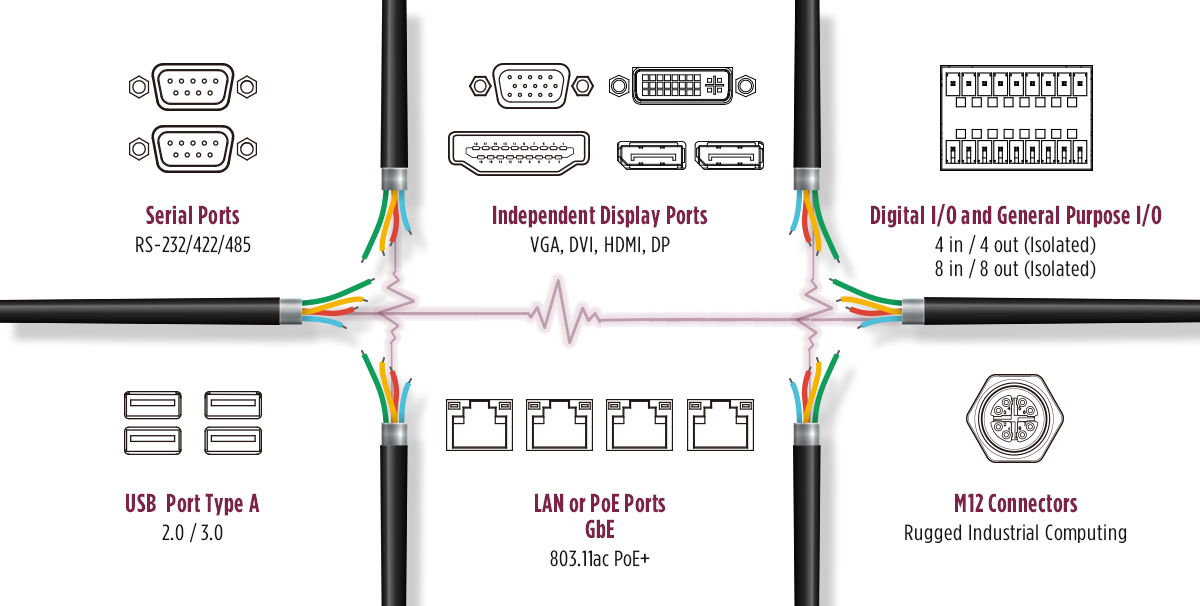
Moreover, rugged computers are configured with various inputs such as USB 3.1 Gen 2 Ports, serial ports, independent display ports, digital and general-purpose I/O, PoE/multiple LAN RJ45, M12, and many more customizable inputs. Also, the COM ports, allow the system to connect with legacy technology. That said, rugged PCs are significantly expandable and flexible compared to standard desktop PCs due to their compact design that still offers expansion features and is configured with a wide array of I/O ports.
Connectivity
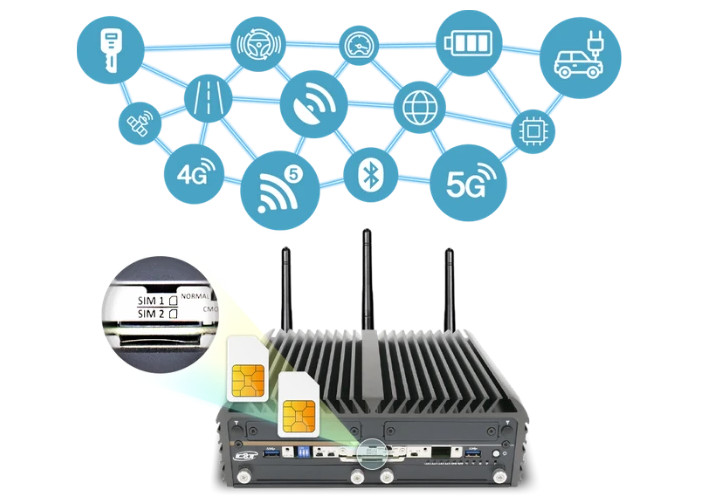
Rugged PCs can be configured with various connections such as Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth, LTE, 4G, and 5G. Wi-Fi 6 can deliver a theoretical top speed of 9.8Gbps, which is 40% faster data transfer than the previous Wi-Fi 5 generation. And for 5G, the theoretical top speed can reach an astonishing 10Gbps, providing a high-bandwidth and low-latency for a reliable performance at a remote place.
Furthermore, systems typically come with dual SIM sockets, allowing organizations to add up to cellular carrier for redundancy. So, in the event that one carrier has a poor signal or no signal at all, the PC can be programmed to connect to a second carrier to offload data to the cloud for remote monitoring and control.