Intel's P-Cores and E-Cores Explained
What is the hybrid core architecture of Intel?
Intel's move to a hybrid CPU design, integrating P cores for high-intensity processing and E cores for energy-efficient tasks, addresses the diverse demands of contemporary computing. This architecture enhances multitasking capabilities, optimizes thermal management, and maintains a competitive edge against rival approaches such as ARM's "big.LITTLE." Intel's combination of performance and efficiency with its heterogeneous cores is tailored to meet both present and anticipated computing needs effectively.
What is P core and E core?
- "P cores," or Performance cores, are a key component of Intel's hybrid CPU architecture debuted in the Alder Lake series, aimed at high-performance tasks. These cores are engineered for demanding computational work, featuring complex designs with sizable caches and sophisticated capabilities to maximize per-thread performance and operate at higher clock speeds. Intel's 12th Gen CPUs incorporate P cores based on the Golden Cove microarchitecture, while the 13th Gen CPUs advance to the Raptor Cove design, succeeding the Cypress Cove cores from the 11th Gen Rocket Lake series.
- "E cores," or Efficiency cores, form part of Intel's newer CPU lineup, intended for handling less intensive tasks while maximizing energy efficiency. These cores are simpler and less power-hungry than their Performance counterparts, enabling the processor to manage everyday applications responsively without unnecessary power consumption or heat production. Intel has utilized the Gracemont microarchitecture for the E cores in both its 12th and 13th Gen CPUs, a successor to the Tremont architecture seen in earlier Pentium Gold and Celeron laptops.
How is P core and E core work together?
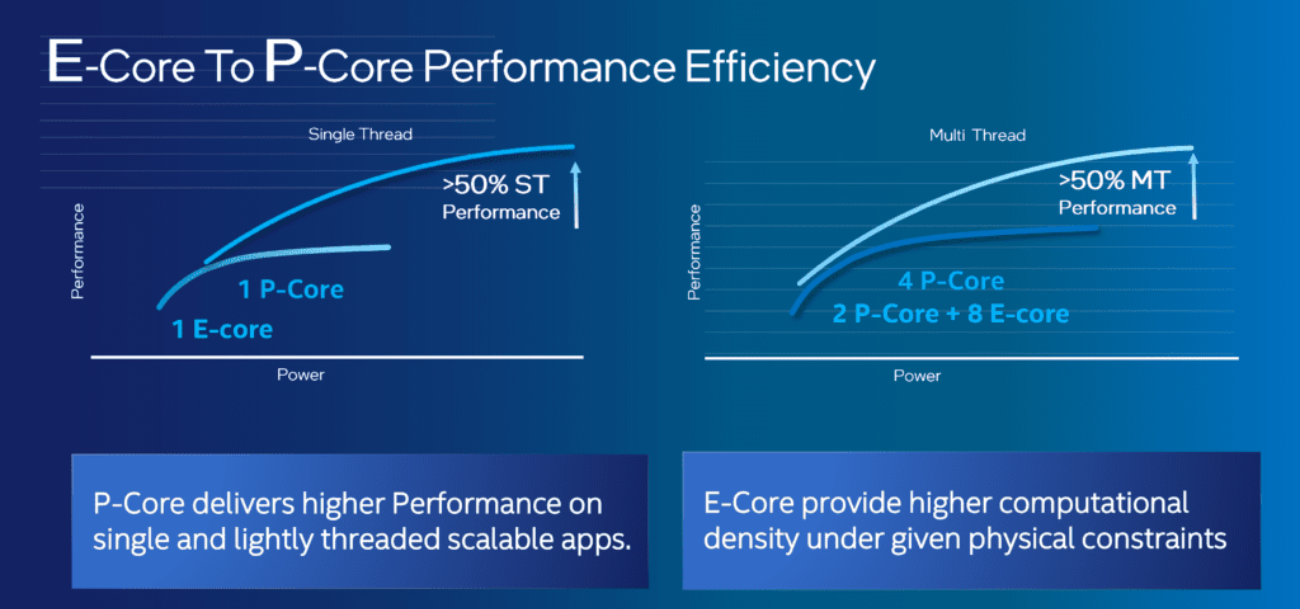
Source: Intel
Intel's innovative CPU design harmonizes the strengths of P and E cores within its hybrid architecture, a significant leap in processor technology. This dual-core approach ensures top-tier performance for demanding tasks and energy-conscious operation for everyday activities. The intelligent collaboration between the two types of cores allows for a responsive adaptation to different computing demands, optimizing both energy usage and computational power. This balance is crucial, with P cores handling the heat of demanding processing while E cores maintain cooler operations for less intensive tasks.
What is the difference between P core and E core?
| Aspect | P-core | E-core |
| Primary Function | Designed for high-performance tasks | Optimized for power efficiency |
| Power Consumption | Higher power usage | Lower energy comsumption |
| Clock Speed | Higher base and boost clock speeds | Operate at lower clock speeds |
| Multithreading | Support Hyper-Threading for multiple threads | Don't support Hyper-Threading |
| Typical Application | Suited for intense processing demands | Geared towards continuos, energy-conscious tasks |
The differentiation of P and E cores illustrates a wider movement in the computing industry towards diverse CPU architectures. This diversity facilitates a flexible and responsive task distribution according to task demands, aiming to optimize the equilibrium of energy use and computational power across different usage situations.
How does the performance of P and E cores compare to Intel's previous architecture?
Intel's 12th Generation chips feature a synergistic mix of Performance (P) and Efficiency (E) Cores. The P-Cores surpass their 11th Generation counterparts by 19% in terms of performance. On the other hand, the E-Cores offer a 40% performance boost over the older Skylake cores at equivalent power consumption levels.Leverage P cores and E cores with Windows 11

Windows 11 is engineered to fully utilize the capabilities of Intel's P and E cores, surpassing Windows 10 in this regard. It incorporates advanced thread scheduling and is integrated with Intel's Thread Director, ensuring tasks are directed to the appropriate core type, whether it's for peak performance or energy efficiency. This leads to improved multitasking, efficient power usage, and a smoother overall user experience, making Windows 11 the ideal platform to harness the potential of Intel's latest hybrid architecture.
Read more: Should You Update Windows 11 from Windows 10 IoT?
How does hybrid architecture affect embedded systems?
Intel's hybrid CPU design revolutionizes embedded systems by merging performance-oriented P cores with energy-efficient E cores. These systems gain a customized balance of power and performance, which is crucial for energy-conscious applications and multitasking demands. This flexible architecture suits a range of embedded uses, from IoT gadgets to industrial machinery, enhancing their lifespan and cost-effectiveness.
C&T’s high-performance industrial computer RCO-6000-RPL Series

RCO-6000-RPL Series is an industrial-grade, fanless computer that leverages Intel's P and E cores for robust edge computing capabilities, even in extreme conditions..
- Intel 13th/12th Gen RPL/ADL CPU
- Intel LGA 1700& R680 Chipset
- DDR5 and PCIe Gen 4 Support
- Support EDGEBoost TechnologiesExplore RCO-6000-RPL Series
FAQs:
Is P core and E core? Which one is better?
Each core type is specialized: P cores excel in high-performance tasks, while E cores are crafted for efficiency and lighter workloads.
Do more CPU cores increase power consumption?
More cores typically mean more power usage, but this varies with the core type and activity. For instance, E cores are designed for lower power consumption.
Can P cores and E cores operate independently?
Indeed, advanced operating systems can now direct tasks to the most fitting core—P or E—using technologies like Intel's Thread Director for optimal efficiency.
Which core is optimal for handling multiple tasks simultaneously?
Both P and E cores play a role in multitasking, with P cores tackling intensive tasks and E cores managing less demanding ones, improving overall multitasking.
What's the thermal impact of using both P and E cores?
This dual-core approach can improve thermal dynamics. E cores tend to run cooler, balancing the heat generated by P cores, which may reduce overall system temperature during mixed workloads.
Are the concepts of P and E cores unique to Intel?
The concept of pairing high-performance with energy-efficient cores is seen in other architectures like ARM's big.LITTLE, but Intel's specific P and E core architecture is proprietary.

