Intel NUC Alternatives: Rugged Industrial-Grade Mini PCs

Semiconductor manufacturers' innovations have led to the production of extremely small and powerful computer components including processors, memory, and storage. This allows computer manufactures to produce highly compact and small form factor PCs that are ideal for developments such as edge computing, IoT, embedded systems, and much more. Such solutions are built with a small form factor while maintaining powerful performance, making them very beneficial for edge computing and IoT solutions that commonly face constraints regarding the size and weight of the implemented devices.
Intel Next Unit of Computing (NUC) is a solution that is produced by Intel to create a powerful small form factor computer. However, the small form factor isn’t the only thing required for deployments within the industrial edge infrastructures. Deployments at the edge commonly experience extreme environmental challenges. Challenges include exposure to extreme heat fluctuation, dirt exposure, up to powerful water jet washdowns. As such, edge computing applications within the industrial sector need to be more than just a small form factor but tested to endure challenging environmental conditions for mission-critical reliability.
This is where rugged mini industrial computers come into place as the best intel NUC alternative for harsh industrial applications. Commercial computers such as the Intel NUC are only meant to be used in a controlled indoor environment, whereas small form factor industrial rugged computers are carefully designed, produced, and validated to endure deployment in extreme environments through a rigorous testing and validation process to ensure their capabilities to withstand extreme environments for a long period of time. That said, this blog post discusses how intel NUC is a good mini PC but not the most suitable option for being deployed in harsh industrial environments.
What is Intel NUC?

Intel Next Unit of Computing or commonly known as Intel NUC is Intel’s innovation for small form factor personal computers that are both powerful and expandable enough for daily personal and office use. Compared to other commercial computers on the market, Intel NUC size is considerably smaller, measuring in at 117 x 112 x 54 [mm] (L x W x H) with a volume of 0.7L for the Intel NUC Pro Mini PC (NUC11TNKv7). Intel NUC is also known for its 4 x 4 inches NUC motherboard form factor which is 30% smaller than the Nano-ITX form factor, a common form factor for smaller-sized motherboards.
The barebones kits are configured with a NUC motherboard, a fan located in the plastic case, a PSU, and a VESA mount. These specs are why Intel NUC is quite a favorable option for indoor computing that requires a palm-sized solution. However, when requiring a small form factor computer for industrial applications, the Intel NUC although powerful, is not suited for rugged reliability in harsh environments like temperature, shock, and vibration. So, if you need a PC that can withstand deployment in challenging environments, you should consider rugged industrial computers as an alternative to Intel’s NUC. Rugged industrial computers are purpose-built for industrial deployments due to their unique characteristics of tackling challenges within the industrial environments. That said, we are going to discuss why rugged mini pcs can be better alternatives to Intel NUCs.
Mini Rugged PCs, 4 Unique Characteristics of NUC Alternatives

Rugged industrial computers are often deployed in extreme environments for extended periods of time while maintaining high-performance, reliability, durability, and longevity. On the other hand, NUC targets workloads more on daily customer usage for well-controlled deployments like in offices, schools, and homes. Both computers offer great performances but the rugged mini PC separates itself from other commercial PC due to several crucial factors that are major benefits for industrial deployments.
1. Fanless & Cable-Less Design

Commercial Mini PCs like the Intel NUC utilize fans as their cooling system, whereas rugged mini PCs utilize a fanless and cable-less design. Although fanlessly cooling down a computer results in better thermals than passive cooling, using a fan can cause many issues that impact a PC's durability and reliability. One rule of thumb when creating a strong and rugged computing solution is to eliminate as many moving parts as possible because reduces the number of parts that fail, making an industrial-grade PC more reliable and durable. Utilizing a fan can increases the risk of downtime and resources to repair or replace the failed or failing fans. Fans are a common point of failure on many electronics, including PCs because they often get clogged with dust, and once they’re clogged, they cause the system to overheat and shut down, requiring maintenance. This is especially problematic for systems deployed in remote locations that cannot be easily accessed.

In contrast, PCs, such as rugged industrial computers have adopted a fanless design that offers various benefits and advantages for rugged computers. By utilizing a fanless design, vent holes are eliminated from the system, increasing a system’s IP rating (ingress protection rating). Due to the adoption of a fanless design, rugged mini PCs are often rated from IP65 up to IP69K. The fanless design also increases MTBF (meant time between failure) and allows for silent operation. Often, the fan turning on and off rapidly during usage can be a major distraction to the user experience. On the other hand, fanless design computers are quiet because they are utilizing heatsinks for passive cooling, eliminating the need for active cooling via fans.

Heat sinks are made out of highly conductive materials capable of dissipating heat away from the hottest component in the motherboard like the CPU away through the outer enclosure. The chassis functions as both a heatsink and as a protective case. Heatsinks are made from aluminum and copper heat pipes to maximize heat dissipation from the CPU to the natural environment. This allows the computer to work silently despite running heavy workloads.
2. Rich I/O and Legacy Technologies

Consumer-grade mini-PCs like the Intel NUC offer generous I/O inputs that are enough for working or gaming purposes. However, industrial applications are still generally configured with legacy technologies. Commercial PCs are only focusing on supporting the latest trend for I/O inputs which creates a huge gap for implementing edge computing for industrial applications. That said, small form-factor industrial computers support a wide array of I/O from the latest ports to legacy ports, to fulfill the customer’s demand for their industrial solutions.
These legacy ports that are disregarded by commercial pc are completely available on industrial pc such as COM ports, serial ports, VGA, DVI, DIO, GPIO, and many more. This is why industrial solutions are implementing rugged mini PCs as alternatives to Intel NUC’s thanks to the availability of both modern and legacy I/O ports.
3. Cable-less, Industrial Components, and SoC

Compact industrial computers adopt a cable-less design to eliminate moving parts that can cause failure during deployments. The removal of cables results in a cleaner system, making it easier to connect to other components without the need for cable routing and cable matching. Also, the removal of cables prevents cabling signal degradation and eliminates latency. To make the computer much more durable for a long time, internal parts of the computer are carefully selected based on the industrial standard components all from resistors, transistors, capacitors, power choke, and many more.
Moreover, rugged mini PCs integrated SoC (system on chip) designs that combine the CPU, GPU, RAM, and more components onto a single silicon board, making the system power-efficient and compact. These detailed additional steps will increase the product lifecycle and lower down the total cost of ownership.
4. Robust Design Structure

To maximize a system’s durability so that it can better withstand exposure to tough shocks and vibrations, small form factor rugged computer chassis are constructed based on a one-piece design. Rugged industrial computers are because they employ a robust structure with fewer joint parts and screws, molded into one piece using extruded heavy-metal creating an ultra-durable solution that’s protected against shocks and vibrations. Moreover, it’s easier to assemble, disassemble, perform maintenance, and create a sealed housing that’s tighter for a higher IP rating performance. The outer enclosure is also dual-purpose, protecting the internal components while working as a giant heatsink dissipating the heat to the natural environment. Compared to the commercial PCs, their outer chassis are mostly made out of plastic and thin aluminum with many parts to construct.
6 Features of Ultra-Rugged PCs (Intel NUC Alternatives)
All of these rugged and robust designs are interconnected to each other in creating an ultimate reliable product with extra durability and performance that lasts for an extended period of time. Here are the rugged features of the rugged mini PC as the Intel NUC alternatives.
1. Extreme Temperature

Consumer-grade computers including the Intel NUC are not capable of withstanding exposure to wide temperature range environments. Regular commercial computers are generally built to work within controlled indoor spaces such as offices and homes. So, deploying these consumer-grade computers in industrial settings jeopardizes the system's safety, often resulting in detrimental downtime. As Intel NUC alternatives, rugged industrial computers are built to withstand a wide range of extreme temperatures. Compared to the Intel NUC's temperature range that ranging from 0℃ to 40℃, rugged mini PCs are capable to withstand extreme heat and cold conditions, ranging from freezing cold -25℃ to scorching hot up to 70℃. This becomes the key for rugged mini PCs to be implemented within industrial applications such as gas and oil rigs, mining, automotive, heavy manufacturing, food, and more.
Learn More About Wide Temperature Range Embedded Systems
2. IP Rating (Ingress Protection)

Due to the fanless design and one-piece architecture, rugged mini PCs are capable of withstanding constant exposure to tiny dust particles and water droplets. Without any ventilation wholes needed for the fan and fewer mounting parts from the one-piece enclosure, rugged mini PCs are rated from IP65 up to IP69K, which is the highest score for the IP rating for both dust particle and water particle exposures. However, this is not the case for Intel NUC because they don’t have an IP rating. After all, the NUC devices aren’t built to withstand harsh environments. So, if you want to deploy a computer that’s capable of surviving challenging environmental conditions that are detrimental to consumer-grade PCs such as the Intel NUC, consider investing in a rugged industrial computing solution as they are ruggedized for challenging environments.
Learn More About IP Rating Embedded System
3. Shock and Vibration Resistance (MIL-STD-810G)

Edge deployments often involve rough situations that involve shocks and vibrations such as in factory automation and the smart automotive industry where the machines are prone to shocks and vibrations. Without any moving parts, means that there are fewer points of failure for the system when exposed to shock and vibration. Thanks to their cable-less design, one-piece chassis, and fanless design, the rugged mini-computers are capable of complying with the military standard MIL-SPEC-810G for shock and vibration resistance. The rugged mini PCs can withstand 50G, Half sine, 11ms (with SSD) in shock, and 5 Grms, 5-500Hz, 0.5 hr/axis (with SSD) in vibration. By complying with the military standard, this indicates that rugged mini-computers are incredibly durable and reliable to be deployed against harsh environments for a long time.
4. Longevity and Versatility

To provide additional protection and ensure that rugged mini PCs perform optimally 24/7, systems are equipped with OVP (over-voltage protection) for input more than 55V, OCP (over current protection), and a wider voltage input ranging from 9V to 48V to cover diverse types of solutions. The I/O are designed with reverse protection to minimize human errors when setting up the system. Moreover, mini rugged PCs are configured with power ignition management for in-vehicle solutions where it can intelligently manage the power fluctuation that occurs in vehicles system.

5. Wireless Connectivity

Edge computing solutions can require remote deployments for their applications. Therefore, for wireless connectivity capabilities, the Intel NUC alternatives are equipped with various connectivity features. However, rugged edge mini computers can be configured with more connectivity that includes Wi-Fi 6, Bluetooth, 4G/LTE, and 5G. Wi-Fi 6 has a theoretical speed of 9.6 Gbps, and 5G connection theoretical speed can reach up to 10Gbps, enabling ultra-fast connections while reducing wireless latency amid remote deployments. Intel NUCs are not equipped with cellular connectivity as are industrial-grade computers. For some remote deployment, cellular connectivity is a requirement to keep your PC connected to the internet.
6. Comprehensive Test and Validation
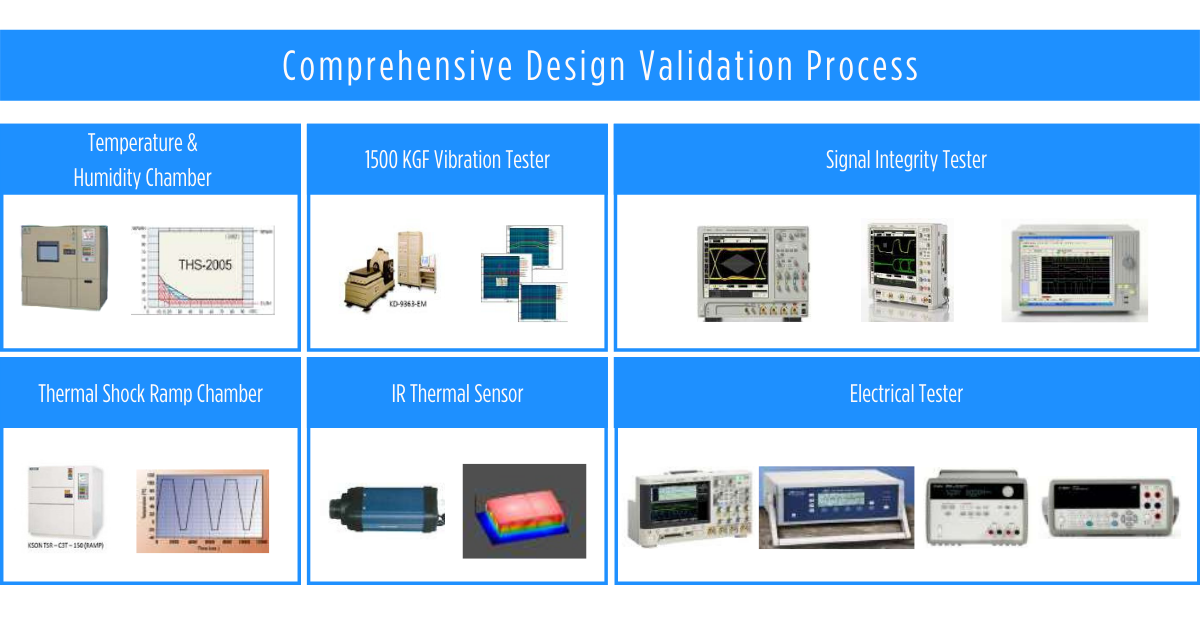
Finally, to completely ensure that the small form factor rugged industrial PC designs are ideal for real-life industrial deployments, devices are rigorously stress tested and validated to ensure optimal performance regardless of where the system is deployed. There are myriad test and validation processes that are tailored in C&T’s testing facilities. These tests are tailored to mimic real-life situations and push the products to their limits. Moreover, rugged mini PCs do not just comply with the MIL-STD-810G standard for shock and vibration, but they are also certified for the electromagnetic interference test. Complying with FCC and CE standards, making sure that the devices are deployable all around the world. Here are our comprehensive design validation machines in our lab testing facilities.

